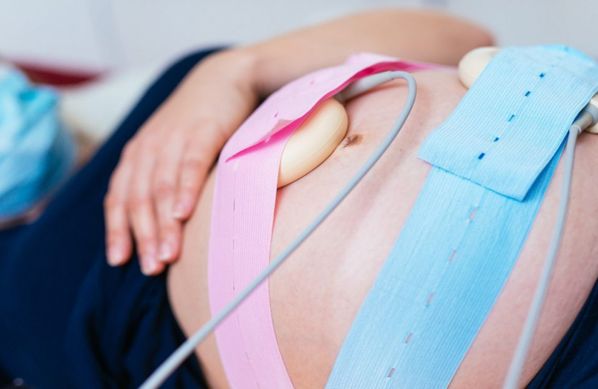
Intrapartum fetal monitoring, commonly referred to as Toco-Cardio Graphy (CTG), is a crucial method used during labor to assess the well-being of the fetus. This monitoring tracks fetal heart rate and uterine contractions to ensure that the baby is tolerating labor well and that there are no signs of fetal distress. Intrapartum fetal monitoring is typically conducted in hospitals or maternity centers with the necessary equipment and trained healthcare professionals. Here are some key aspects of intrapartum fetal monitoring (Toco-Cardio Graphy):
Monitoring Techniques: Intrapartum fetal monitoring involves the use of external or internal devices to monitor both the fetal heart rate and uterine contractions. External monitoring includes attaching two sensors to the mother's abdomen: one for tracking the fetal heart rate and another for measuring the strength and frequency of contractions. Internal monitoring may be used in certain situations where a small electrode is placed on the baby's scalp for more accurate heart rate readings.
Continuous vs. Intermittent Monitoring: Depending on the pregnancy risk level and labor progression, fetal monitoring can be either continuous or intermittent. Continuous monitoring is more common in high-risk pregnancies or when complications arise during labor, while intermittent monitoring may be sufficient for low-risk pregnancies. Healthcare providers determine the best approach based on the individual circumstances of the labor.
Real-Time Assessment of Fetal Well-Being: The primary purpose of Toco-Cardio Graphy is to provide real-time information about the baby’s condition during labor. The fetal heart rate is analyzed in relation to uterine contractions, helping healthcare providers identify any signs of fetal distress, such as irregular heart rate patterns, that may indicate the need for medical intervention.
Customized Monitoring Plans: Each labor is unique, and healthcare providers tailor the monitoring plan according to the mother’s and fetus's specific needs. For high-risk pregnancies or labor complications, continuous and more detailed monitoring may be required, whereas low-risk pregnancies may only need intermittent monitoring.
Education and Counseling on Fetal Monitoring: Prior to labor, expectant mothers are informed about the purpose of fetal monitoring and what to expect during the procedure. Healthcare providers explain the benefits of CTG, the monitoring equipment, and potential outcomes based on the readings. This helps women understand how monitoring contributes to a safe delivery.
Identifying and Managing Complications: Intrapartum fetal monitoring is crucial for identifying potential complications during labor, such as fetal hypoxia (lack of oxygen) or distress. If abnormalities are observed in the fetal heart rate, healthcare providers may recommend interventions like changing the mother's position, administering oxygen, or initiating emergency delivery procedures to safeguard the baby’s health.
Emotional Support During Monitoring: Labor can be a stressful experience, especially when monitoring indicates potential complications. Healthcare providers offer emotional support to mothers during the process, helping them understand what is happening and why certain interventions may be necessary. This reassurance can reduce anxiety and foster a sense of control over the labor experience.
Delivery and Post-Delivery Care: If fetal monitoring indicates that the baby is tolerating labor well, delivery proceeds normally. In cases where distress is detected, the healthcare team may opt for a cesarean or assisted delivery to ensure the safety of both mother and baby. Post-delivery, the baby's condition is further assessed to ensure a smooth transition after birth.
Post-Delivery Monitoring: After a painless delivery, the healthcare team continues to monitor the mother for any side effects of the epidural, such as headaches or temporary numbness. The recovery process is generally smooth, and the mother can enjoy bonding with her newborn without significant discomfort from labor.
Postpartum Monitoring for Mother and Baby: After delivery, healthcare providers continue to monitor the well-being of both the mother and newborn. Any issues identified during fetal monitoring are addressed in the postpartum period to ensure the health and safety of both.
Intrapartum fetal monitoring through Toco-Cardio Graphy plays a vital role in modern childbirth, providing essential insights into the baby’s well-being during labor. By offering real-time data on fetal heart rate and contractions, this monitoring allows healthcare providers to make informed decisions that promote a safe and healthy delivery.
Dr. Ravneet Kaur Offers a comprehensive range of obstetrics and gynaecology treatments, utilizing advanced techniques and personalized care to support patients on their journey to reproductive health and wellness.

High-risk pregnancy care refers to specialized medical services aimed at monitoring and managing pregnancies with increased risks due to various factors.

Painless delivery, also known as epidural analgesia, refers to the use of pain relief methods during labor to help women manage the discomfort of childbirth.

Intrapartum fetal monitoring, commonly referred to as Toco-Cardio Graphy (CTG), is a crucial method used during labor to assess the well-being of the fetus.
Recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL) refers to the occurrence of two or more consecutive miscarriages, and it affects a small percentage of women trying to conceive.

Menopausal treatment focuses on managing the symptoms and health risks associated with menopause, which marks the end of a woman's reproductive years.
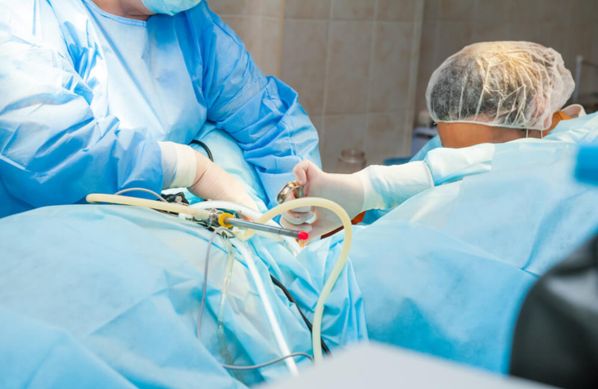
Laparoscopically Assisted Vaginal Hysterectomy (LAVH) is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to remove the uterus.
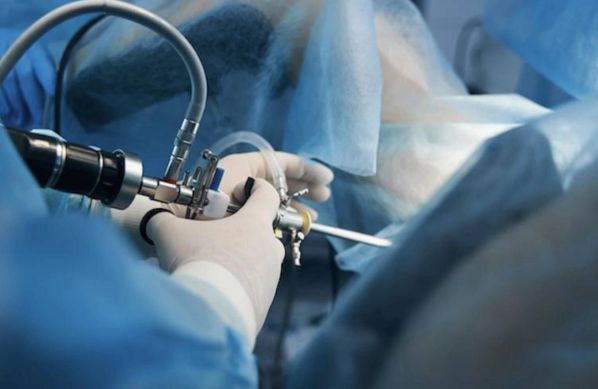
Laparoscopy and hysteroscopy are minimally invasive surgical procedures used to diagnose and treat various gynaecology conditions.
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is a sophisticated assisted reproductive technology (ART) that enables individuals or couples facing fertility challenges to conceive a child.
Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) is a widely used assisted reproductive technology (ART) that involves placing sperm directly into a woman’s uterus during her ovulation period.

Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) is a specialized form of assisted reproductive technology (ART) used to address male infertility issues.

