Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) is a widely used assisted reproductive technology (ART) that involves placing sperm directly into a woman’s uterus during her ovulation period. This procedure is designed to increase the chances of conception by facilitating the sperm's journey to the egg. IUI is often recommended for couples experiencing infertility due to various factors, including low sperm count, ovulatory disorders, or unexplained infertility. Here are some key aspects of Intrauterine Insemination (IUI):
Indications for IUI: IUI is typically indicated for individuals or couples facing the following fertility challenges:
Low Sperm Count or Motility: Conditions where sperm quality or quantity is insufficient for natural conception.
Unexplained Infertility: Cases where no identifiable cause of infertility is found after extensive testing.
Ovulatory Disorders: Irregular or absent ovulation that may hinder natural conception.
Cervical Issues: Conditions affecting the cervix, such as scarring or mucus problems, that may impede sperm passage.
Single Women: Cases where no clear cause of infertility is identified after extensive testing.
Genetic Disorders: IUI is commonly used by single women seeking to conceive with donor sperm.
Pre-IUI Assessment and Counseling: Before undergoing IUI, a thorough evaluation is conducted to determine the underlying causes of infertility. This assessment may include medical history, physical examinations, hormonal evaluations, and imaging studies, such as ultrasounds. Counseling is crucial, as it helps individuals or couples understand the IUI process, discuss expectations, and address any emotional concerns.
Ovarian Monitoring and Induction: In many cases, ovarian stimulation is employed to enhance the chances of successful ovulation and increase the number of eggs available for fertilization. Fertility medications, such as clomiphene citrate or gonadotropins, may be prescribed. Monitoring through blood tests and ultrasounds is performed to track ovarian response and determine the optimal time for insemination.
Sperm Preparation: On the day of the IUI procedure, a sperm sample is collected from the male partner or a sperm donor. The sperm is then processed in the laboratory to separate the most motile and healthy sperm from the rest. This preparation enhances the likelihood of successful fertilization by ensuring only the best sperm are used during the insemination.
Insemination Procedure: The IUI procedure is typically performed in a medical office and is relatively quick and painless. A thin, flexible catheter is used to place the prepared sperm directly into the woman’s uterus during her ovulation window. This bypasses the cervix, allowing the sperm to be positioned closer to the eggs for optimal chances of fertilization.
Post-IUI Monitoring: After the insemination, patients are often advised to rest briefly before resuming normal activities. Follow-up care typically includes blood tests to check hormone levels and confirm whether pregnancy has occurred. Patients are encouraged to monitor for any early pregnancy symptoms and report any concerns to their healthcare provider.
Risks and Considerations: IUI is generally considered a safe procedure with minimal risks. However, potential complications may include infection, cramping, or bleeding. Multiple pregnancies may also occur, especially when fertility medications are used. Healthcare providers discuss these risks with patients to ensure informed decision-making.
Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) offers a less invasive option for individuals and couples facing fertility challenges, providing a pathway to conception.
Dr. Ravneet Kaur Offers a comprehensive range of obstetrics and gynaecology treatments, utilizing advanced techniques and personalized care to support patients on their journey to reproductive health and wellness.

High-risk pregnancy care refers to specialized medical services aimed at monitoring and managing pregnancies with increased risks due to various factors.

Painless delivery, also known as epidural analgesia, refers to the use of pain relief methods during labor to help women manage the discomfort of childbirth.
Intrapartum fetal monitoring, commonly referred to as Toco-Cardio Graphy (CTG), is a crucial method used during labor to assess the well-being of the fetus.
Recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL) refers to the occurrence of two or more consecutive miscarriages, and it affects a small percentage of women trying to conceive.

Menopausal treatment focuses on managing the symptoms and health risks associated with menopause, which marks the end of a woman's reproductive years.
Laparoscopically Assisted Vaginal Hysterectomy (LAVH) is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to remove the uterus.
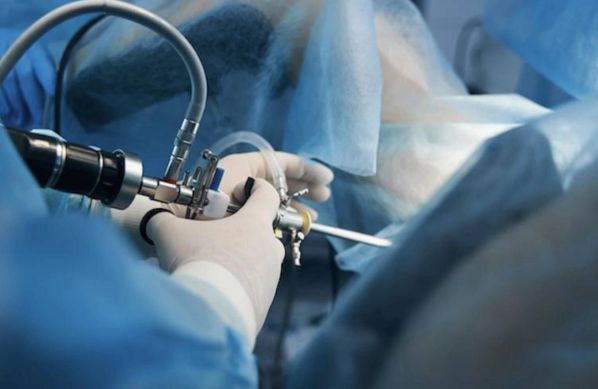
Laparoscopy and hysteroscopy are minimally invasive surgical procedures used to diagnose and treat various gynaecology conditions.
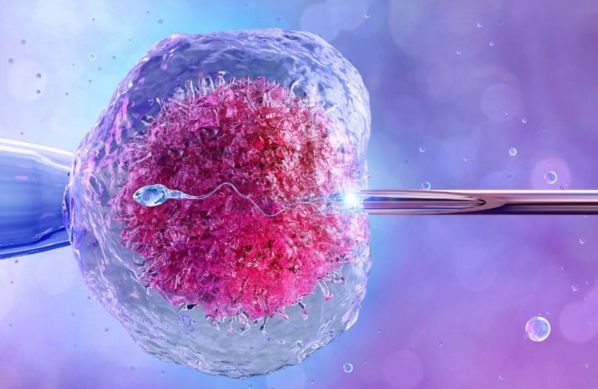
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is a sophisticated assisted reproductive technology (ART) that enables individuals or couples facing fertility challenges to conceive a child.

Intrauterine Insemination (IUI) is a widely used assisted reproductive technology (ART) that involves placing sperm directly into a woman’s uterus during her ovulation period.

Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) is a specialized form of assisted reproductive technology (ART) used to address male infertility issues.

